Compression Ratio And Octane Chart
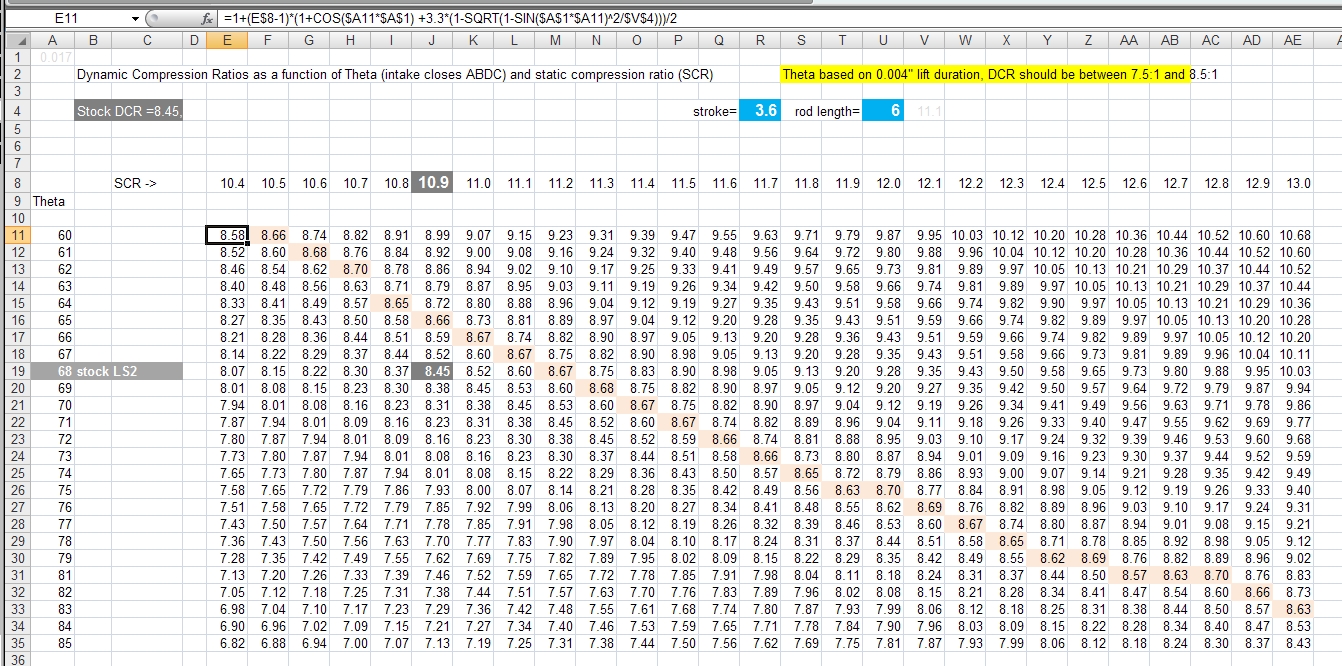
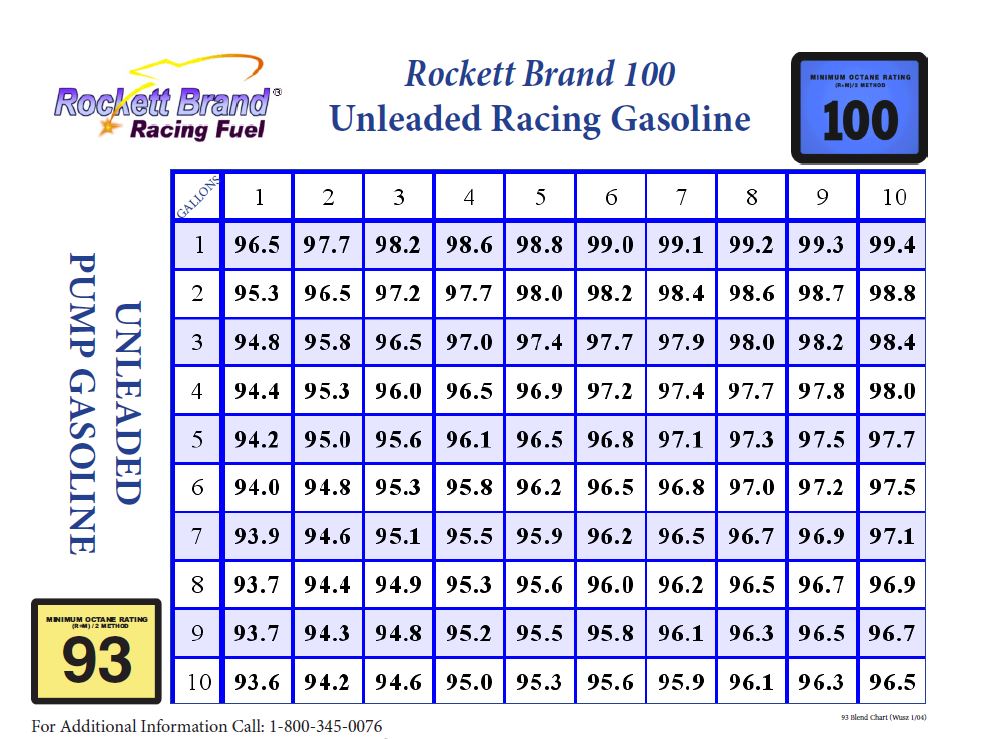
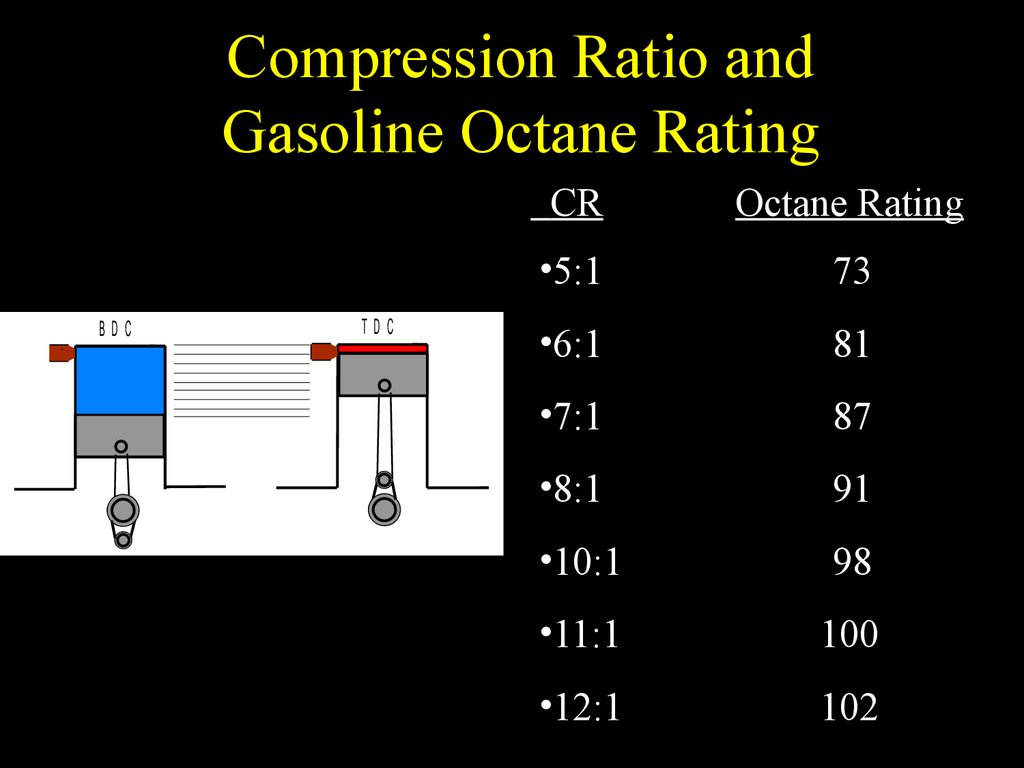
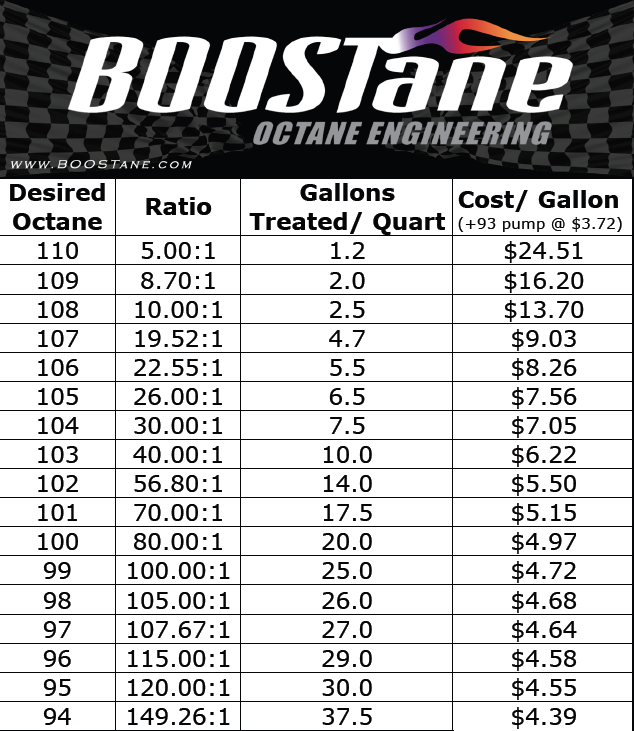
Compression Ratio And Octane Chart - Average octane rating based on refiner sales volumes and is based on a calendar year. Web the compression ratio calculator finds both the static and the dynamic compression ratio of your combustion engine. Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in the graph below) was likely due to refinery technology improvement and the addition of lead, which guards against engine. Check out the size, engine, technology, cargo space, and more! Stations are required to post them on bright yellow stickers on each pump. Web octane levels of gasoline have dovetailed with these increases. This is why some engines require 100+ octane with an 11:1 compression ratio while others are perfectly fine on 91 octane with a 13:1. Web the ideal octane level for an 11 to 1 compression engine is typically 91 or higher. High octane fuels don’t burn hotter. It’s important to be mindful of the octane level when refueling to prevent any engine damage. Web at its core, octane rating is simply a scale that defines a fuel’s tolerance for compression. (a compression ratio in an engine is the ratio of the cylinder's combustion chamber divided by the total volume of the cylinder). Web get your engine's optimal compression ratio and total displacement in no time flat! Lower octane fuels may increase the risk of engine knocking or detonation, which can damage the engine. Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: Web this chart shows the final compression ratio by combining the static compression ratio of an engine and the maximum blower boost from the blower system. Web the ideal octane level for an 11 to 1 compression engine is typically 91 or higher. To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need about. These calculators are rough approximations and none of the numbers here are absolute. This is why some engines require 100+ octane with an 11:1 compression ratio while others are perfectly fine on 91 octane with a 13:1. Web get your engine's optimal compression ratio and total displacement in no time flat! As such, fuels with a higher octane rating (95, 98 etc.) are higher performance fuels than lower rated fuels (93). Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which would further improve engine efficiency. Web from the 1920s to the 1970s, the evolution of engines. Web this chart shows the final compression ratio by combining the static compression ratio of an engine and the maximum blower boost from the blower system. Optional on ex premium package and gt1 package. (a compression ratio in an engine is the ratio of the cylinder's combustion chamber divided by the total volume of the cylinder). Web an 8.5:1 compression. Web the ideal octane level for an 11 to 1 compression engine is typically 91 or higher. Web calculate the minimum gasoline fuel octane required based on your engine's compression ratio, maximum boost pressure, spark advance, and air fuel ratio. Then follow our mixing charts provide our calculator app, above. Web the oem compression ratio is ideal for the minimum. As such, fuels with a higher octane rating (95, 98 etc.) are higher performance fuels than lower rated fuels (93). High octane fuels don’t burn hotter. This tends to be true for older, traditional engines with less effective combustion chambers. Web at its core, octane rating is simply a scale that defines a fuel’s tolerance for compression. Lower octane fuels. View features and specs for each trim level of the 2024 kia k5 sedan. Then follow our mixing charts provide our calculator app, above. Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: (a compression ratio in an engine is the ratio of the cylinder's combustion chamber divided by the total volume of the cylinder). Web use the. Web the octane number is a measure of how resistant the fuel is to detonation, which is very bad for an engine that is designed to run on gasoline and so must be avoided. Stations are required to post them on bright yellow stickers on each pump. Web at its core, octane rating is simply a scale that defines a. Web octane levels of gasoline have dovetailed with these increases. (a compression ratio in an engine is the ratio of the cylinder's combustion chamber divided by the total volume of the cylinder). To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need about. As such, fuels with a higher octane rating (95, 98 etc.). Just complete your engine setup, click calculate, and you’re on your way to maximum performance. Web the octane number is a measure of how resistant the fuel is to detonation, which is very bad for an engine that is designed to run on gasoline and so must be avoided. This tends to be true for older, traditional engines with less. Web an 8.5:1 compression ratio can typically run on regular 87 octane fuel. This tends to be true for older, traditional engines with less effective combustion chambers. Web one way to estimate the actual static compression ratio is by using a simple formula that produces a result referred to as effective compression ratio (ecr). High octane fuels don’t burn hotter.. Web one way to estimate the actual static compression ratio is by using a simple formula that produces a result referred to as effective compression ratio (ecr). Web an 8.5:1 compression ratio can typically run on regular 87 octane fuel. To determine octane to your compression, follow our. Web the compression ratio calculator finds both the static and the dynamic. Web higher octane levels can enable higher compression ratios, which would further improve engine efficiency. Web at its core, octane rating is simply a scale that defines a fuel’s tolerance for compression. Web an octane rating is defined as the standard measure of the performance of a motor fuel. The higher the rating, the more tolerant of high compression. View features and specs for each trim level of the 2024 kia k5 sedan. Web it's easy to find what octane rating a gas has: Lower octane fuels may increase the risk of engine knocking or detonation, which can damage the engine. Click ahead to discover what compression ratio is and how an engine can alert you to knocking and pinging. To get 8.0:1 with the preceding rod, stroke, and cam intake closing event, you would need about. (a compression ratio in an engine is the ratio of the cylinder's combustion chamber divided by the total volume of the cylinder). Average octane rating based on refiner sales volumes and is based on a calendar year. There are many other factors such as head. This tends to be true for older, traditional engines with less effective combustion chambers. Web higher octane fuels are often required or recommended for engines that use a higher compression ratio and/or use supercharging or turbocharging to force more air into the engine. Gasoline octane improvement during that period (red markers in the graph below) was likely due to refinery technology improvement and the addition of lead, which guards against engine. Web octane levels of gasoline have dovetailed with these increases.Compression Ratio To Octane Chart
Compression Ratio To Octane Chart
Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart A Visual Reference of Charts
Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart
The Octane Game
Mechanical Engineering Octane Number
Vp Racing Fuel Octane Chart
Engine Components and Operation презентация онлайн
Fuel Octane Compression Ratio Chart
Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart
Web The Oem Compression Ratio Is Ideal For The Minimum Octane Rating Of Gasoline Recommended, For The Factory Power Output Levels, For Factory Boost Levels, For Emission Compliance And For A Driving Pattern That The Oem Believes Will Be Driven.
This Simple Formula Converts The Amount Of Boost To Additional Compression Ratio As If The Engine Were Normally Aspirated.
To Determine Octane To Your Compression, Follow Our.
Web Use The Standard Compression Ratio Fuel Octane Chart To Know The Fuel Suitable For Your Engine.
Related Post: