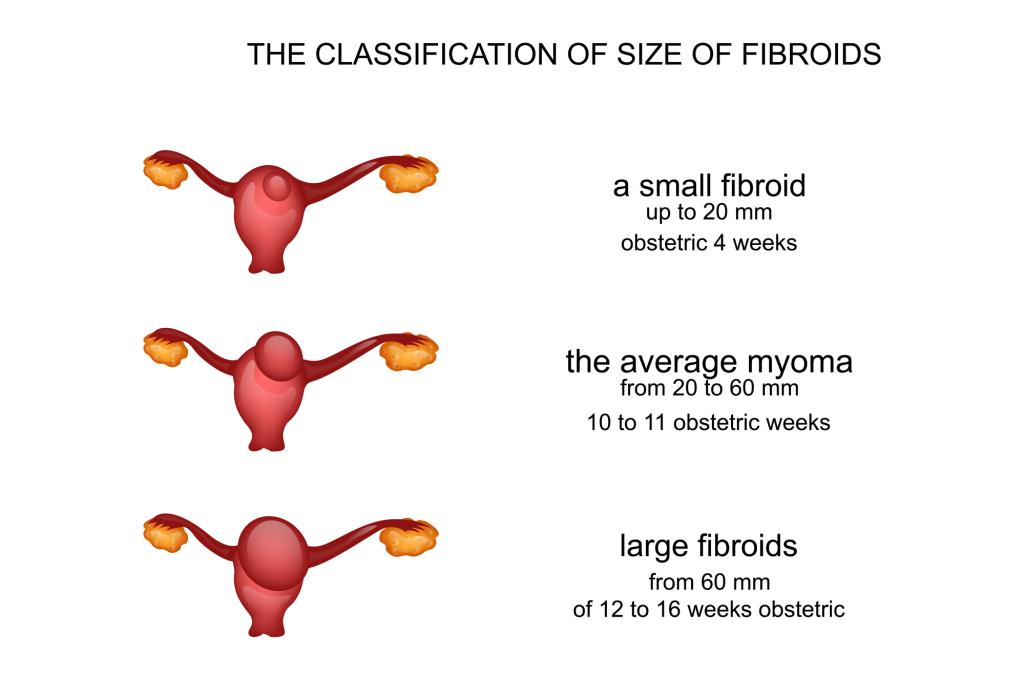
Fibroid Sizes Chart In Cm
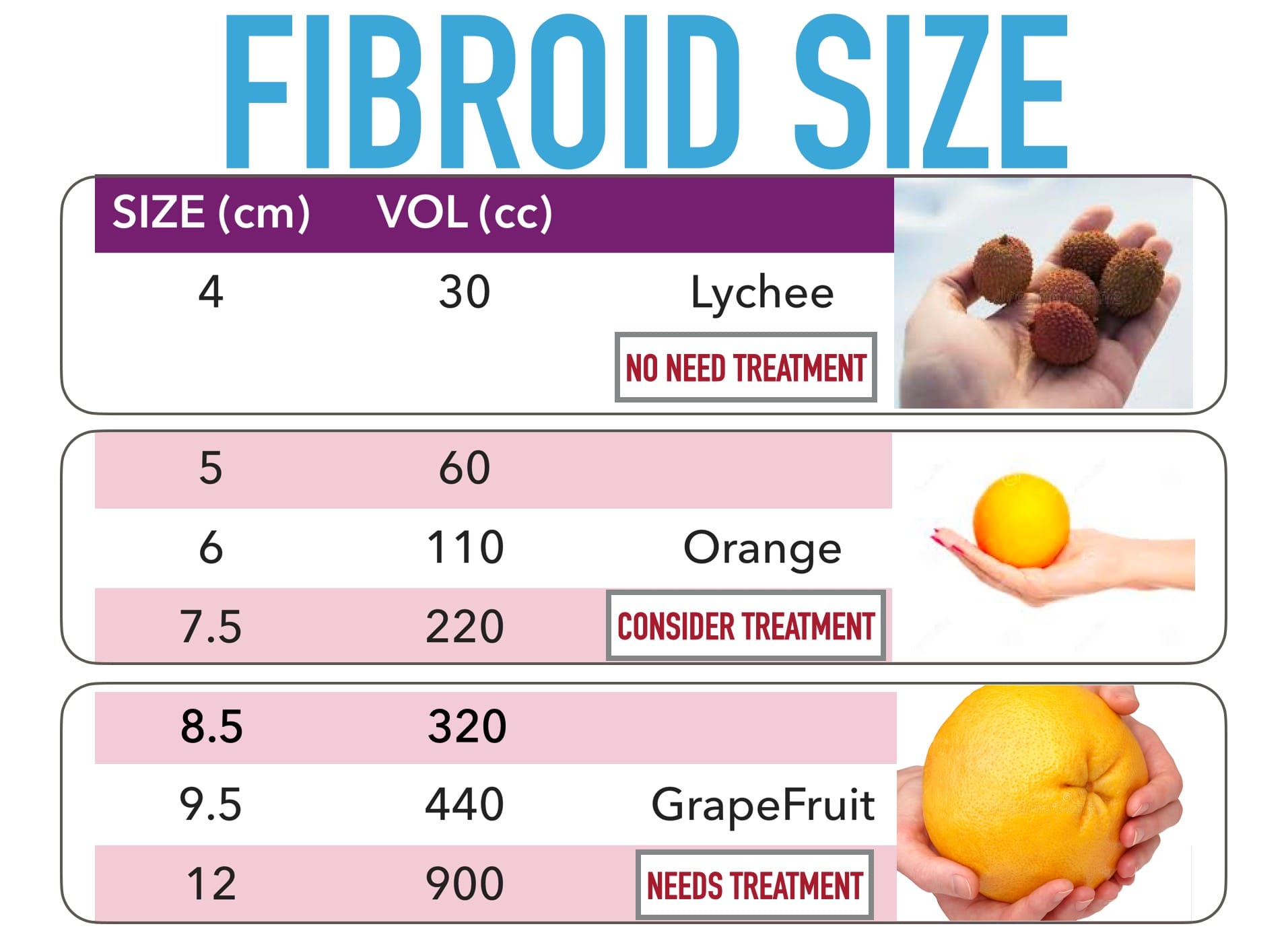
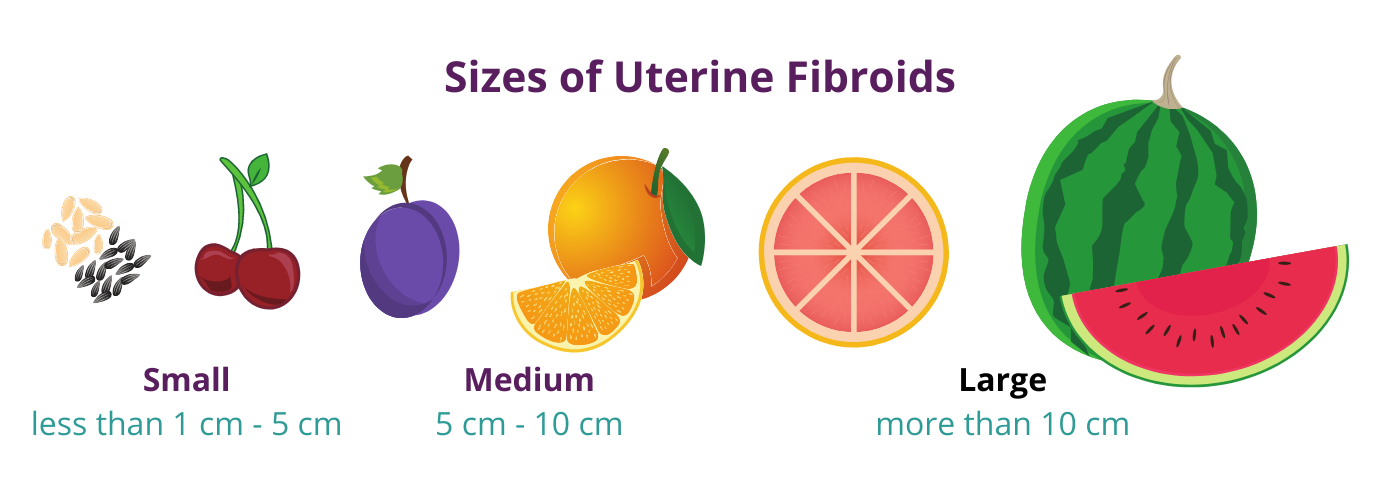
Fibroid Sizes Chart In Cm - Web updated on january 29, 2024. They are typically found during a routine pelvic exam and often diagnosed between ages 30 and 40, though they can develop at any age. These growths can develop within the wall of your uterus, inside the main cavity of your uterus or on the outer surface of your uterus. Some research has found that the incidence of polyp cancer is up to 75% when a polyp reaches 35 mm (3.5 cm). Web is there any size chart to measure the size of fibroids? In some extreme cases, fibroids weighing more than 20 pounds have been reported. Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the muscle tissue of the uterus. Web use the following guide as a reference point to generalize the size of fibroids from small, medium, and large. “watchful waiting” is the usual course of treatment for most fibroids, particularly if they aren’t causing any symptoms. Web to better explain the different sizes of fibroids, here is a chart to reference: Large (10cm+) size of a mango to a watermelon. Web uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) growths in or around the uterus. For comparison, fibroids can be as small as a seed or get as large as a watermelon. They are typically found during a routine pelvic exam and often diagnosed between ages 30 and 40, though they can develop at any age. These massive growths are rare but can become large enough to significantly distort the shape of the uterus. Web this fibroid tumor size chart offers a helpful visual guide: Large fibroids exceed 10 cm in diameter, and depending on their location, could begin to put pressure on surrounding organs. Depending on the type and other factors, up to 50% of polyps over 20 mm (2 cm) are cancerous. Web fibroids classification by size includes small fibroids less than 2 cm, medium fibroids at 2 to 5 cm, and large fibroids greater than 5 cm. Web schedule an appointment. As fibroids increase in size, their impact on the body. Web uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are the most common benign tumours in women. By age 50 nearly 70% of white women and more than 80% of black women have had at least one fibroid. First, take a deep breath. Web the risk that a polyp will become cancerous can continue to. For ease of classification, doctors refer to the size of a uterine fibroid utilizing a quick reference chart. Large fibroids can measure 10 centimeters (or more!) and may require more intensive treatment. As fibroids increase in size, their impact on the body. Although uterine fibroids can reach any size, giant fibroids are rare. Web schedule an appointment. Web valerie lynn baker, m.d. Uterine fibroids, also referred to as leiomyomas or myomas, are growths in the uterus or on the uterine wall. Web uterine fibroid size chart. They may be single or multiple and their size varies from a few millimetres to 30 cm or more. Ranging in size from a plum to an orange Medically reviewed by cordelia nwankwo, md. Ranging in size from a seed to a cherry medium: Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the muscle tissue of the uterus. Web uterine fibroid size can vary from less than an inch to larger than a grapefruit. The largest fibroid ever documented in a living patient was the size of a pumpkin and. Web for example, a fibroid that is the size of a blueberry or 2 centimeters can take between four to five years to become twice its original size resembling the size of a cherry. Web use the following guide as a reference point to generalize the size of fibroids from small, medium, and large. It’s possible to have one fibroid. Large fibroids exceed 10 cm in diameter, and depending on their location, could begin to put pressure on surrounding organs. Uterine fibroids, also referred to as leiomyomas or myomas, are growths in the uterus or on the uterine wall. Web this fibroid tumor size chart offers a helpful visual guide: Web updated on january 29, 2024. Web uterine leiomyomas (fibroids). How large can fibroids get? Web clusters of fibroids can range in size from 1 millimeter to more than 20 centimeters (8 inches) in diameter or even larger. Web this fibroid tumor size chart offers a helpful visual guide: Web uterine fibroid size chart. Black women are more likely to have fibroids — and more severe symptoms — than are. Web fibroids are noncancerous tumors that grow in the smooth muscle cells of the uterus. Ranging in size from a plum to an orange Medically reviewed by cordelia nwankwo, md. Web uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are the most common benign tumours in women. Web fibroids classification by size includes small fibroids less than 2 cm, medium fibroids at 2 to 5. Web learn about fibroid locations, different fibroid types, and fibroid size classifications. Web to better explain the different sizes of fibroids, here is a chart to reference: Web is there any size chart to measure the size of fibroids? Black women are more likely to have fibroids — and more severe symptoms — than are white women. Web updated on. Web uterine fibroid size chart. Large fibroids exceed 10 cm which is 3.9 inches in diameter. It’s possible to have one fibroid or several, as they are located on the uterus’s surface, in. First, take a deep breath. Web uterine leiomyomas (fibroids) are the most common benign tumours in women. “watchful waiting” is the usual course of treatment for most fibroids, particularly if they aren’t causing any symptoms. Depending on the type and other factors, up to 50% of polyps over 20 mm (2 cm) are cancerous. Web the risk that a polyp will become cancerous can continue to rise with the size of the polyp. It’s possible to have one fibroid or several, as they are located on the uterus’s surface, in. For ease of classification, doctors refer to the size of a uterine fibroid utilizing a quick reference chart. Web for example, a fibroid that is the size of a blueberry or 2 centimeters can take between four to five years to become twice its original size resembling the size of a cherry. The largest fibroid ever documented in a living patient was the size of a pumpkin and weighed over 100 lbs. They are typically found during a routine pelvic exam and often diagnosed between ages 30 and 40, though they can develop at any age. Fibroids are common and usually occur between the ages of 30 and 40. Your fibroid size impacts your treatment options. Web uterine fibroids are noncancerous (benign) growths in or around the uterus. As fibroids increase in size, their impact on the body. Uterine fibroids are noncancerous growths of the muscle tissue of the uterus. Black women are more likely to have fibroids — and more severe symptoms — than are white women. First, take a deep breath. For the vast majority of patients, the answer is no.Intramural Fibroid Size Chart
Fibroids Anthony Siow
Fibroid Sizes Chart In Mm
A Visual Guide To Fibroid Sizes USA Fibroid Centers
Uterine Fibroid Size Chart In Cm
Uterine Fibroids How Fast Do They Grow & What Size Do They Reach?
Intramural Fibroid Size Chart
A Visual Guide To Fibroid Sizes USA Fibroid Centers
Fibroid Tumor Size Chart
Fibroid Sizes Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
In Some Extreme Cases, Fibroids Weighing More Than 20 Pounds Have Been Reported.
Web Fibroids Vary In Size, Ranging From 1.1 Cm To As Large As A Grapefruit Before Being Discovered.
Web Learn About Fibroid Locations, Different Fibroid Types, And Fibroid Size Classifications.
Uterine Fibroids, Also Referred To As Leiomyomas Or Myomas, Are Growths In The Uterus Or On The Uterine Wall.
Related Post: