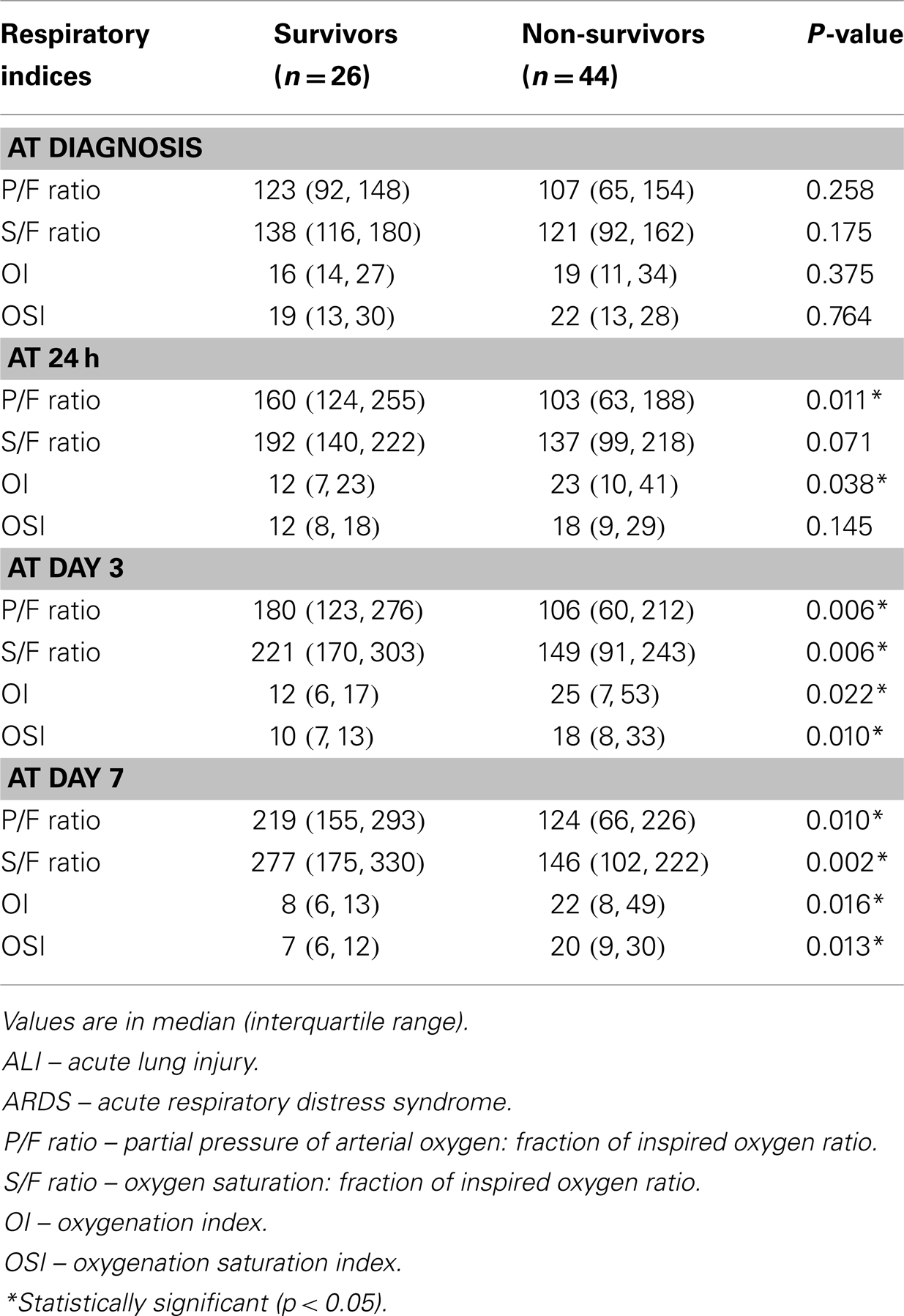
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart
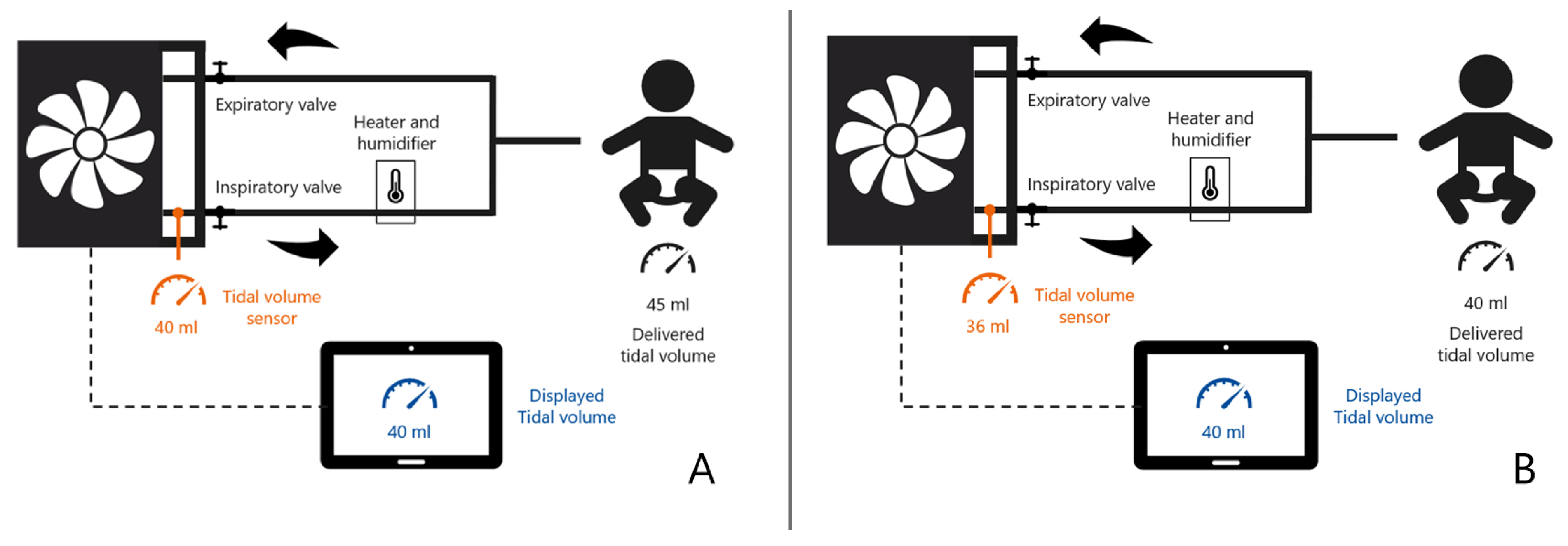
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart - Web the endotracheal tube (ett) depth and tidal volume calculator estimates depth of optimal ett placement and target tidal volume by height. Web we aimed to compare 4 methods of ibw calculation and determine level of agreement between methods and impact of measurement variance on tidal volumes (tv) prescribed in mechanically ventilated pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (pards). Devine formula (1974) tidal volume calculator. Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Currently, pneumotachography is the most commonly utilized bedside technology. Web assigning tidal volume for all patients < 5 feet tall. This will be done by using the ml/kg value documented in the patient’s medical chart. Web this calculator determines the optimal endotracheal tube placement (based on patient height) to avoid right mainstem intubation, hypoxemia, and pneumothorax (when ett is placed too deeply) or injury to vocal cords or accidental. Individual ventilator settings should be guided by monitoring gas exchange with blood gas information when available or pulse oximetry using an fio 2 less than 0.3 and capnography. (3) the accuracy of the compliance. Normal pediatric respiratory rates by age Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ards, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ards. Web this calculator determines the optimal endotracheal tube placement (based on patient height) to avoid right mainstem intubation, hypoxemia, and pneumothorax (when ett is placed too deeply) or injury to vocal cords or accidental. Web tidal volumes standardized to predicted body weight are recommended for adult mechanical ventilation, but children are frequently ventilated by using measured body weight. Currently, pneumotachography is the most commonly utilized bedside technology. Ideal body weight (ibw) / tidal volume chart 6 ml/kg 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 290 300 310 330 340 360 370 380 400 410 420 440 450 470 480 490 510 520 530 550 560 580 590 600 males male 22.4 (2) the site of tidal volume measurement within the breathing circuit; Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper threshold of 560ml of tidal volume necessary for lung protective ventilation of. Web the ventilator may deliver a tidal volume that is higher or lower than the one set by the user. Currently, pneumotachography is the most commonly utilized bedside technology. Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper threshold of 560ml of tidal volume necessary for lung protective ventilation of. Web with this tidal volume calculator, you may calculate both tidal volume ranges, determined by your. Web tidal volumes standardized to predicted body weight are recommended for adult mechanical ventilation, but children are frequently ventilated by using measured body weight. (1) the phase during which the tidal volume is measured (inspiration versus expiration); Devine formula (1974) tidal volume calculator. Web this project will inform a future project that will prospectively calculate, in children mechanically ventilated, tidal. Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ards, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ards. Web accurate measurement of delivered tidal volumes in infants and children is essential during mechanical ventilation.. Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper threshold of 560ml of tidal volume necessary for lung protective ventilation of. Normal pediatric respiratory rates by age (3) the accuracy of the compliance. Individual ventilator settings should be guided by monitoring gas exchange with blood gas. Individual ventilator settings should be guided by monitoring gas exchange with blood gas information when available or pulse oximetry using an fio 2 less than 0.3 and capnography. Web ibw calculations based on the b. Web the endotracheal tube (ett) depth and tidal volume calculator estimates depth of optimal ett placement and target tidal volume by height. Web the chart. This will be done by using the ml/kg value documented in the patient’s medical chart. Web the ventilator may deliver a tidal volume that is higher or lower than the one set by the user. (3) the accuracy of the compliance. Web accurate measurement of delivered tidal volumes in infants and children is essential during mechanical ventilation. Web the chart. Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper threshold of 560ml of tidal volume necessary for lung protective ventilation of. Ideal body weight (ibw) / tidal volume chart 6 ml/kg 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 290 300. Web tidal volumes standardized to predicted body weight are recommended for adult mechanical ventilation, but children are frequently ventilated by using measured body weight. Ibw calculations based on the b. Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Currently, pneumotachography is the most commonly utilized bedside technology. (3). Web the chart below is a guide, adapted from those recommendations and current clinical practice at nationwide children’s. Ibw calculations based on the b. (1) the phase during which the tidal volume is measured (inspiration versus expiration); Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper. Web this calculator determines the optimal endotracheal tube placement (based on patient height) to avoid right mainstem intubation, hypoxemia, and pneumothorax (when ett is placed too deeply) or injury to vocal cords or accidental. (3) the accuracy of the compliance. Web tidal volumes standardized to predicted body weight are recommended for adult mechanical ventilation, but children are frequently ventilated by. Currently, pneumotachography is the most commonly utilized bedside technology. This will be done by using the ml/kg value documented in the patient’s medical chart. Web the chart below is a guide, adapted from those recommendations and current clinical practice at nationwide children’s. Web the endotracheal tube (ett) depth and tidal volume calculator estimates depth of optimal ett placement and target tidal volume by height. Web this calculator determines the optimal endotracheal tube placement (based on patient height) to avoid right mainstem intubation, hypoxemia, and pneumothorax (when ett is placed too deeply) or injury to vocal cords or accidental. Web tidal volumes standardized to predicted body weight are recommended for adult mechanical ventilation, but children are frequently ventilated by using measured body weight. Web this project will inform a future project that will prospectively calculate, in children mechanically ventilated, tidal volumes based on different weight measurement techniques (actual, ideal body weight [ibw]): Web the ventilator may deliver a tidal volume that is higher or lower than the one set by the user. Ibw calculations based on the b. Web ltvv is an approach that targets tidal volume between 6 and 8 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for patients without acute respiratory distress syndrome or ards, and 4 to 6 milliliters per kilogram of predicted body weight for those with ards. Web ibw calculations based on the b. Web the endotracheal tube (ett) depth and tidal volume calculator estimates depth of optimal ett placement and target tidal volume by height. Web tidal volumes (v t) can be measured continuously by monitoring airflow signals of assisted ventilation. Web there are four major factors to consider when interpreting the measured tidal volumes that are reported by the ventilator: Ideal body weight (ibw) / tidal volume chart 6 ml/kg 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 270 290 300 310 330 340 360 370 380 400 410 420 440 450 470 480 490 510 520 530 550 560 580 590 600 males male 22.4 Web the adult bvm provided a mean tidal volume of 807.7ml versus the pediatric bvm providing 630.7ml, both of which exceeded the upper threshold of 560ml of tidal volume necessary for lung protective ventilation of.Figure 2 from Does Size Matter When Calculating the “Correct” Tidal
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Neonatal Tidal Volume Chart
JCM Free FullText Tidal Volume in Pediatric Ventilation Do You
Daily Low Tidal Volume Ventilation Data Collection Tool Agency for
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart
Pediatric Tidal Volume Chart
[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Tidal Volume
Neonatal Tidal Volume Chart
(1) The Phase During Which The Tidal Volume Is Measured (Inspiration Versus Expiration);
(2) The Site Of Tidal Volume Measurement Within The Breathing Circuit;
Normal Pediatric Respiratory Rates By Age
Individual Ventilator Settings Should Be Guided By Monitoring Gas Exchange With Blood Gas Information When Available Or Pulse Oximetry Using An Fio 2 Less Than 0.3 And Capnography.
Related Post:



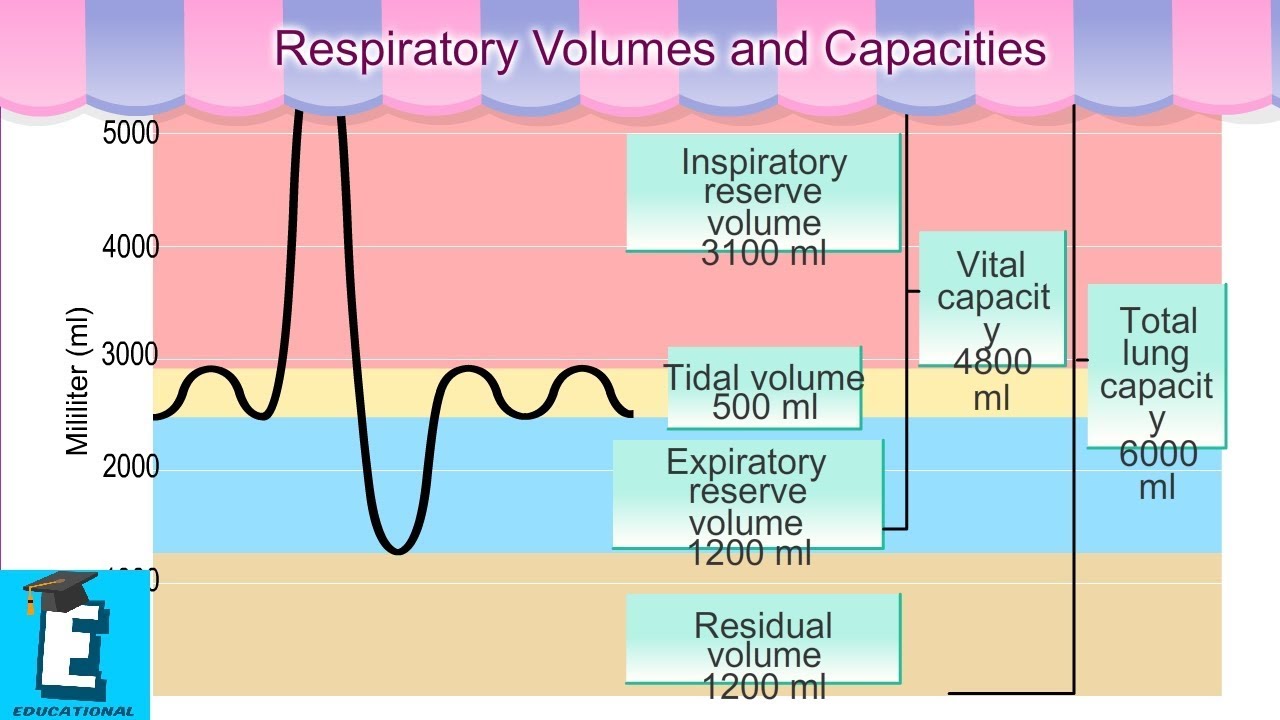


![[DIAGRAM] Diagram Of Tidal Volume](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/e4af828c6418a7e44bc8372f315c35f487d02d87/3-Figure1-1.png)
