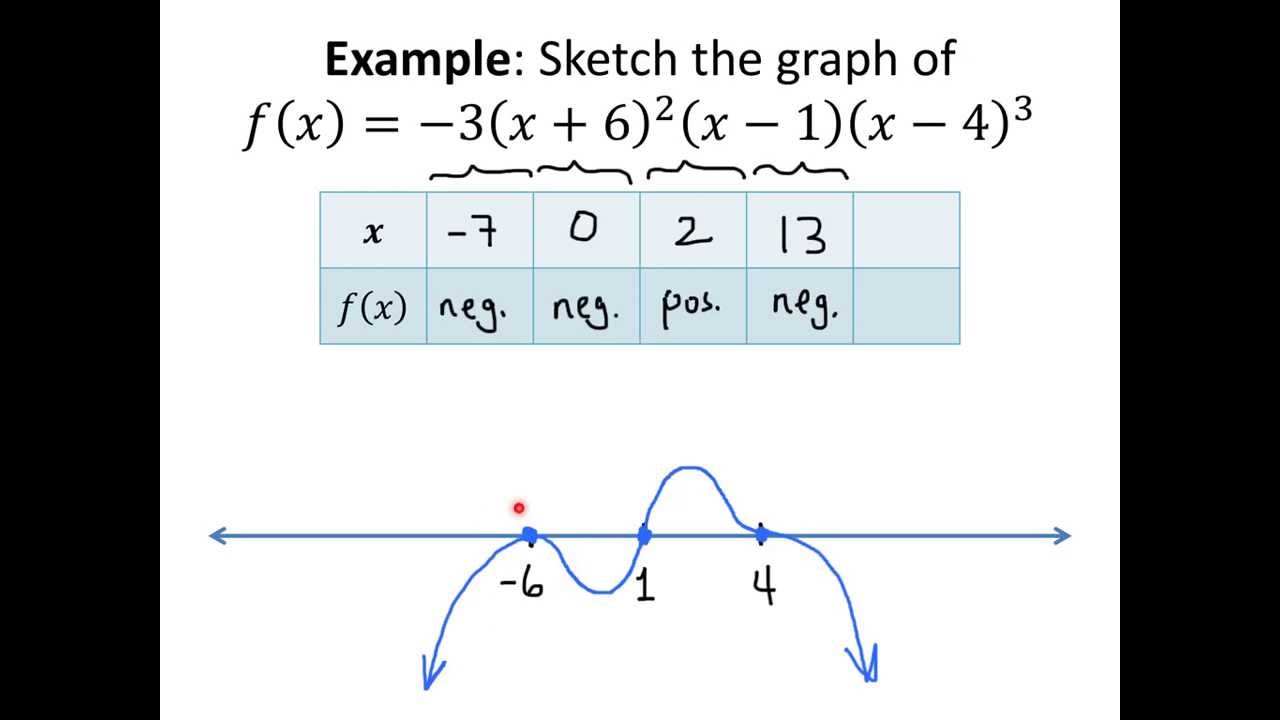
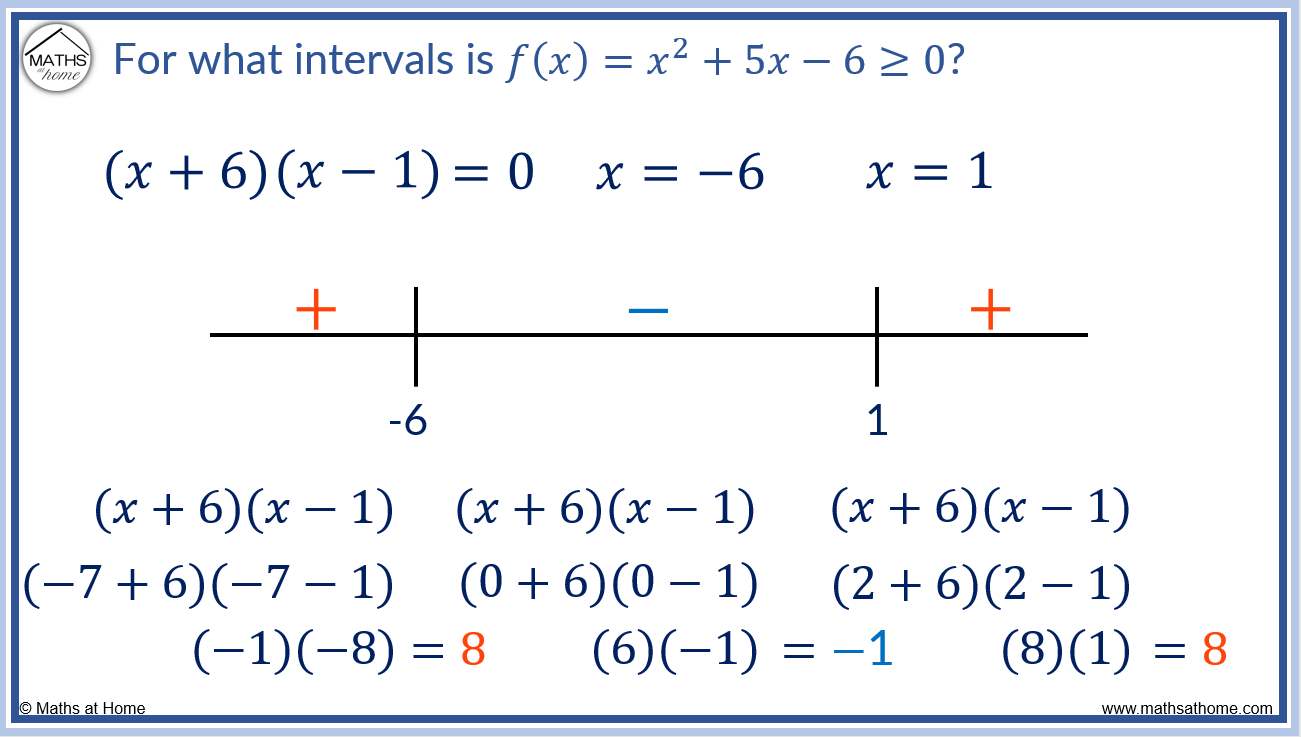
Sign Chart Calculus
Sign Chart Calculus - It could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or equal, but the process is not much effected. Use first derivative test and the results of step 2 2 to determine whether f f has a local maximum, a local minimum, or neither at each of the critical points. Note that these can be written as. Select a value of x from each interval and compute f(x). The f'(𝑥) sign diagram displays intervals for which the function is increasing or decreasing. Web to construct a sign chart of a function $f$ in a interval $i = (a,b)$ or $[a,b]$, you need the requirement that $f$ is continuous in $i$. Web review how we use differential calculus to find the intervals where a function increases or decreases. Finding decreasing interval given the function. Web a comprehensive collection of the most notable symbols in calculus and analysis, categorized by topic and function into charts and tables along each symbol's meaning and example. Web please look at my chart and tell me if i have it set up correctly. Begin by finding all special values of the polynomial. By examining the intervals where the function is positive, negative, or zero, sign charts aid in identifying critical points, determining the behavior of. It could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or equal, but the process is not much effected. To establish a sign chart (number lines) for f ' , first set f ' equal to zero and then solve for x. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. This method is based on the following: How do i find increasing & decreasing intervals with differential calculus? Note that these can be written as. Find critical points get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Web graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Download an example notebook or open in the cloud. A job posting from the company for a dietary aid in the pittsburgh area puts the pay at $16 an hour. Select a value of x from each interval and compute f(x). You can ignore the 1/12, since it is a positive constant. (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t). Intervals on which a function is increasing or decreasing. The intervals you want are (−∞, −2) ( − ∞, − 2), (−2, 3) ( − 2, 3), and (3, ∞) ( 3, ∞). You can ignore the 1/12, since it is a positive constant. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into. Note that these can be written as. Web a comprehensive collection of the most notable symbols in calculus and analysis, categorized by topic and function into charts and tables along each symbol's meaning and example. Finding decreasing interval given the function. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. Web. (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t) > 0. For example, of the type. Web graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Finding increasing interval given the derivative. How do i find increasing & decreasing intervals with differential calculus? Web signs and sign charts the other method is to use a sign chart with the signs of the factors. This method is based on the following: Use first derivative test and the results of step 2 2 to determine whether f f has a local maximum, a local minimum, or neither at each of the critical points. Recognize that. A job posting from the company for a dietary aid in the pittsburgh area puts the pay at $16 an hour. In this case, the second derivative test is inconclusive, meaning that we must use a difference scheme to determine if x = 0 is in fact an inflection point. And our goal is to figure out which function is. Select a value of x from each interval and compute f(x). Increasing & decreasing intervals review. Finding increasing interval given the derivative. Web summary of sign analysis technique 1. Web an inflection point (or point of inflection) is the point at which the concavity of the graph changes sign. The intervals where a function is increasing (or decreasing) correspond to the intervals where its derivative is positive (or negative). Since sign chart is based on bolzano's theorem. In this case, the second derivative test is inconclusive, meaning that we must use a difference scheme to determine if x = 0 is in fact an inflection point. + + =. How do i find increasing & decreasing intervals with differential calculus? Complete documentation and usage examples. By examining the intervals where the function is positive, negative, or zero, sign charts aid in identifying critical points, determining the behavior of. For example, of the type (ax+b) (gx+h) (px+q) (sx+t)>0 it could also be less than or less than or equal or. All the signs should be positive, since the square of a nonzero real number is positive. Finding increasing interval given the derivative. Web please look at my chart and tell me if i have it set up correctly. Find critical points get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Web how to create a sign chart to determine where a. Get a grid of sign charts for a function and its first and second derivatives. This will divide the domain into intervals. The f'(𝑥) sign diagram displays intervals for which the function is increasing or decreasing. Web an inflection point (or point of inflection) is the point at which the concavity of the graph changes sign. It could also be less than or less than or equal or greater than or equal, but the process is not much effected. Web sign charts are used to analyze functions or solve inequalities. Find critical points get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Web summary of sign analysis technique 1. Web this is an example of how to use sign charts in precalculus and calculus to help locate critical points and graph behavior. How do i find increasing & decreasing intervals with differential calculus? Web they provide a concise way to understand the sign of a function within specific intervals. Web sign chart is used to solve inequalities relating to polynomials, which can be factorized into linear binomials. (ax +b)(gx + h)(px + q)(sx + t) > 0. 1 a linear factor, ax + b, will be zero at one point (x = b a) and will be positive on one side of the zero and negative on the other. Web review how we use differential calculus to find the intervals where a function increases or decreases. In this case, the second derivative test is inconclusive, meaning that we must use a difference scheme to determine if x = 0 is in fact an inflection point.How to Understand Sign Diagrams
Sign Chart Math A Visual Reference of Charts Chart Master
Solving Inequalities Using sign chart Calculus 1 YouTube
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
Sign chart calculus qustmama
What is a sign chart in calculus?
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
How to Understand Sign Diagrams
+ + = + + + = + + = + = + = + = = + = +
Use First Derivative Test And The Results Of Step 2 2 To Determine Whether F F Has A Local Maximum, A Local Minimum, Or Neither At Each Of The Critical Points.
All The Signs Should Be Positive, Since The Square Of A Nonzero Real Number Is Positive.
Web Here Are The Basics Of How To Create A Sign Chart And How To Use It To Solve Inequalities.
Related Post: