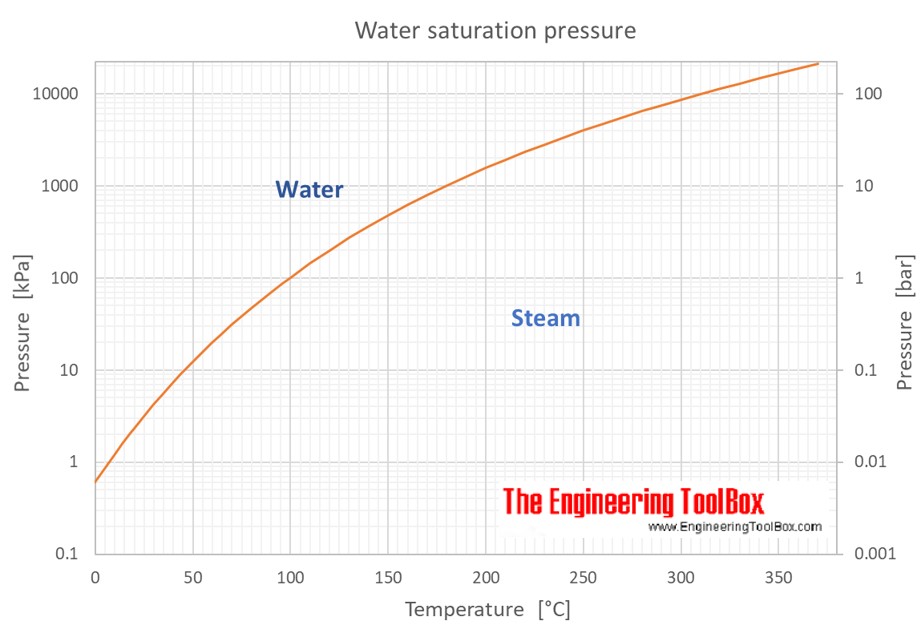
Water Vapour Pressure Chart
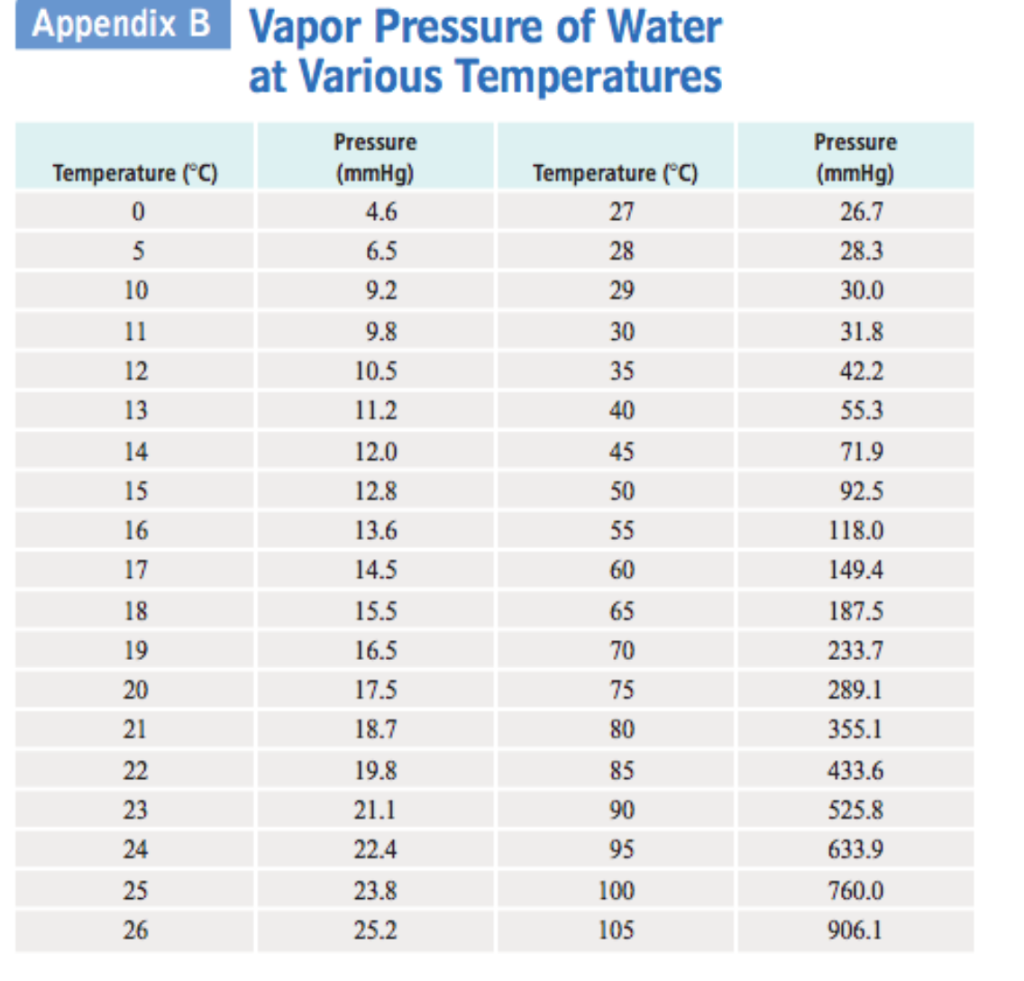
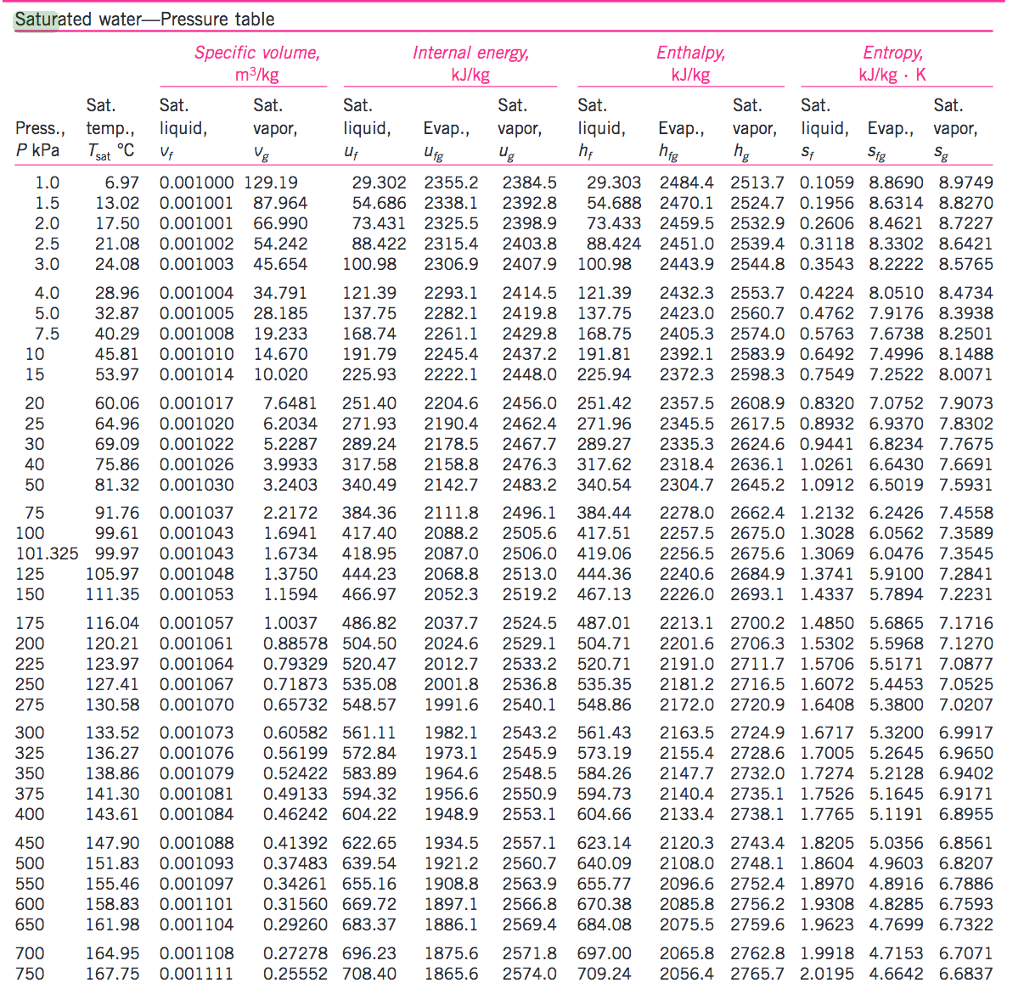
Water Vapour Pressure Chart - Using this 1st calculator, you insert temperature in °f, and get the vapor pressure of water in terms of kpa, psi, mmhg, bar, atm, torr. Web for example, air at sea level, and saturated with water vapor at 20 °c, has partial pressures of about 2.3 kpa of water, 78 kpa of nitrogen, 21 kpa of oxygen and 0.9 kpa of argon, totaling 102.2 kpa, making the basis for standard atmospheric pressure. Web from crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 65th edition (rounded to two decimal places) temp, °c. Pressure (degrees c) (mmhg) (degrees c) (mmhg) Web figure 2 2: Crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 84th edition (2004). Web the vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in gaseous form (whether pure or in a mixture with other gases such as air). Web explore a comprehensive table of water vapor pressure at different temperature values presented in both si (kpa) and us customary (psi) units. The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Web this formula is illustrated in a phase diagram — a chart showing how phases change and coexist at equilibrium at different pressures and temperatures. Vapour pressure is also called the vapour tension. Generally a substance's vapor pressure increases as temperature increases and decreases as temperature decreases (i.e. Using this 1st calculator, you insert temperature in °f, and get the vapor pressure of water in terms of kpa, psi, mmhg, bar, atm, torr. Crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 84th edition (2004). The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Web water vapour pressure table at different temperatures. It is the pressure exerted by the saturated vapour in contact with the surface of the liquid at that temperature. The pressure up cancels the pressure down and boiling begins. Atomic parameters (ie, ea, d,.) thermodynamic data. Vapor pressure is directly proportional to temperature). We look at the 68°f example specifically. The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. Vapour pressure is also called the vapour tension. Web the vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in. Generally a substance's vapor pressure increases as temperature increases and decreases as temperature decreases (i.e. We look at the 68°f example specifically. Vapor pressure is directly proportional to temperature). Web vapor pressure of water (mmhg) source of data: Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. Web saturated vapor pressure, density for water. Web figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). Web the vapor pressure of water at room temperature (25 ° c) is 23.8 mm hg, 0.0313 atm, or 23.8 torr, or 3.17. At its freezing point (0 ° c), the vapor pressure of water is 4.6 torr. Web vapor pressure of water from 0 °c to 100 °c. This chart shows the general relationship between a substance's vapor pressure and temperature change. Web water boiling temperature vs pressure in vacuum table chart. We look at the 68°f example specifically. Web figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. We look at the 68°f example specifically. Vapor pressure of water. Web for example, air at sea level, and saturated with water vapor at 20 °c, has partial pressures of about 2.3 kpa of water, 78 kpa of nitrogen, 21 kpa of oxygen and 0.9 kpa of argon, totaling 102.2 kpa, making the basis for standard atmospheric pressure. Below are some selected values of temperature and the saturated vapor pressures required. Web figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. Vapor pressure of water is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by libretexts. Pressure. The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. Web vapor pressure of water (mmhg) source of data: Web the vapor pressure of water at room temperature (25 ° c) is 23.8 mm hg, 0.0313 atm, or 23.8 torr, or. Web vapor pressure of water. Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. This chart shows the general relationship between a substance's vapor pressure and temperature change. Crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 84th edition (2004). Web vapor pressure of h 2 o at various temperatures (celsius) note that when water vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure, then the. Crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 84th edition (2004). Web saturated vapor pressure, density for water. Web the vapor pressure of water at room temperature (25 ° c) is 23.8 mm hg, 0.0313 atm, or 23.8 torr, or 3.17 kpa. Web the vapor pressure of water is the pressure exerted by molecules of water vapor in gaseous form (whether pure. Web with this vapor pressure of water calculator, you can find the vapor pressure at a particular temperature according to five different formulas. Water at high pressure has a higher boiling point than when that water is at atmospheric pressure. Web figures and tables showing how the properties of water changes along the boiling/condensation curve (vapor pressure, density, viscosity, thermal conductivity, specific heat, prandtl number, thermal diffusivity, entropy and enthalpy). It is the pressure exerted by the saturated vapour in contact with the surface of the liquid at that temperature. The pressure up cancels the pressure down and boiling begins. Web this formula is illustrated in a phase diagram — a chart showing how phases change and coexist at equilibrium at different pressures and temperatures. The saturation vapor pressure is the pressure at which water vapor is in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed state. Web vapor pressure of water. Crc handbook of chemistry and physics, 84th edition (2004). Generally a substance's vapor pressure increases as temperature increases and decreases as temperature decreases (i.e. Vapor pressure of water is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by libretexts. Below are some selected values of temperature and the saturated vapor pressures required to place the boiling point at those temperatures. At its boiling point (100 ° c), the vapor pressure of water is 658.0 torr (atmospheric pressure). Saturation (pressure) 11 p, mpa t, °c density, kg/m3 ρ l ρ v enthalpy, kj/kg h lv ∆h entropy, kj/(kg·k) s l s v ∆s volume, cm3/g v v 611.657 pa 0.01 999.79 0.004 855 0.00 2500.9 2500.9 0.000 00 9.1555 9.1555 1.000 21 205 991. Vapor pressure is measured in the standard units of pressure. Using this 1st calculator, you insert temperature in °f, and get the vapor pressure of water in terms of kpa, psi, mmhg, bar, atm, torr.Vapour Pressure Of Water Chart
Vapor Pressure Chart For Water
How do you find vapor pressure of water at given temperature? Socratic
Water Vapour Pressure Chart Bar
Vapour Pressure Of Water Chart
[PDF] Vapor Pressure Formulation for Water in Range 0 to 100 °C. A
Vapor Pressure Chart For Water
Vapor Pressure Chart For Water
Conservation physics Fundamental microclimate concepts
Water Vapour Pressure Chart Bar
This Chart Shows The General Relationship Between A Substance's Vapor Pressure And Temperature Change.
Vapour Pressure Is Also Called The Vapour Tension.
Vapor Pressure Is Directly Proportional To Temperature).
Web For Example, Air At Sea Level, And Saturated With Water Vapor At 20 °C, Has Partial Pressures Of About 2.3 Kpa Of Water, 78 Kpa Of Nitrogen, 21 Kpa Of Oxygen And 0.9 Kpa Of Argon, Totaling 102.2 Kpa, Making The Basis For Standard Atmospheric Pressure.
Related Post:

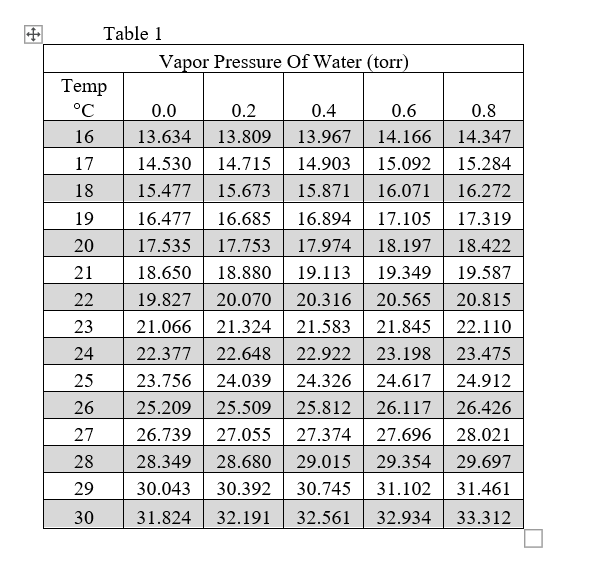
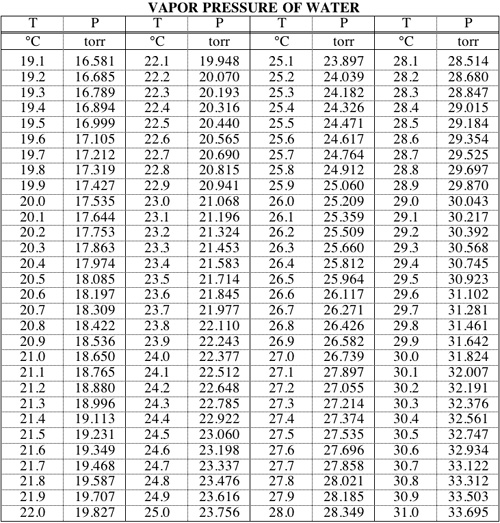

![[PDF] Vapor Pressure Formulation for Water in Range 0 to 100 °C. A](https://d3i71xaburhd42.cloudfront.net/471011a1b864be3f78720f4d8ba4f21385acd117/8-Table7-1.png)