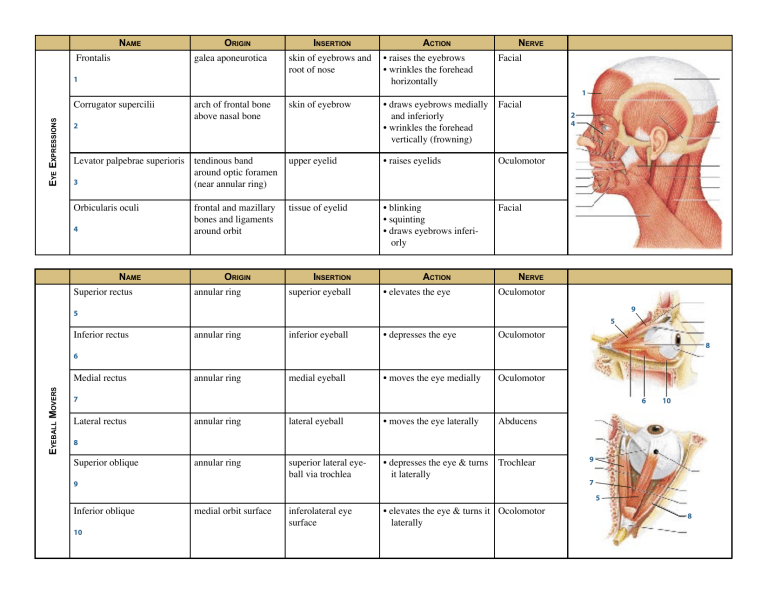
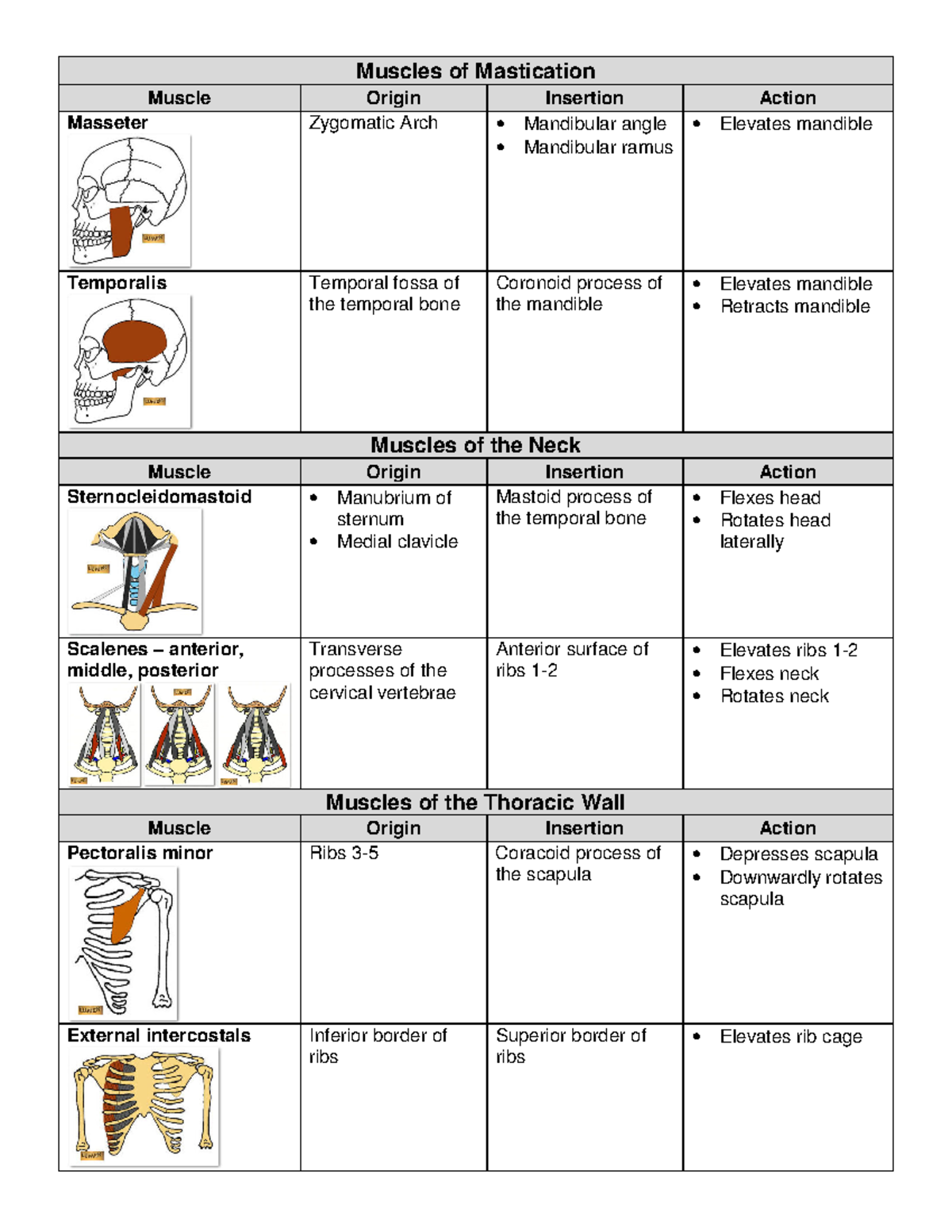
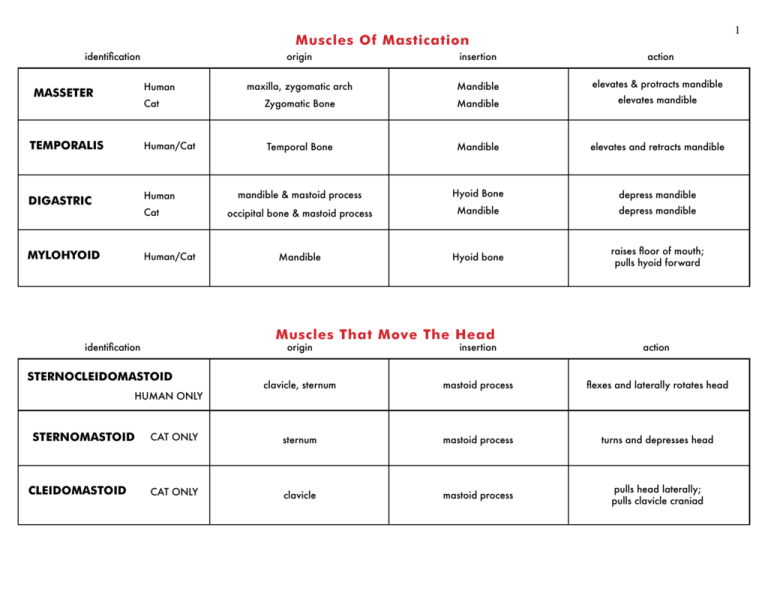
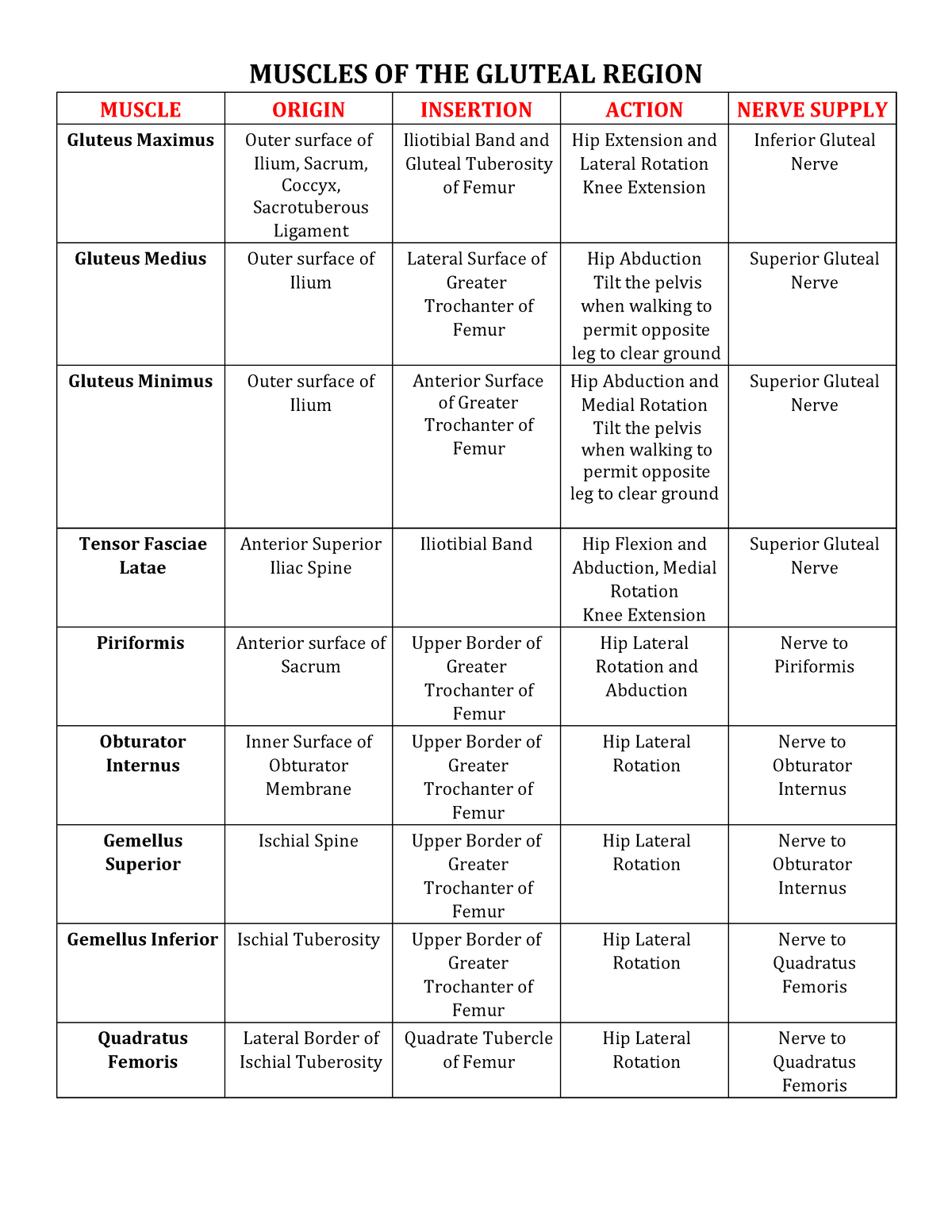
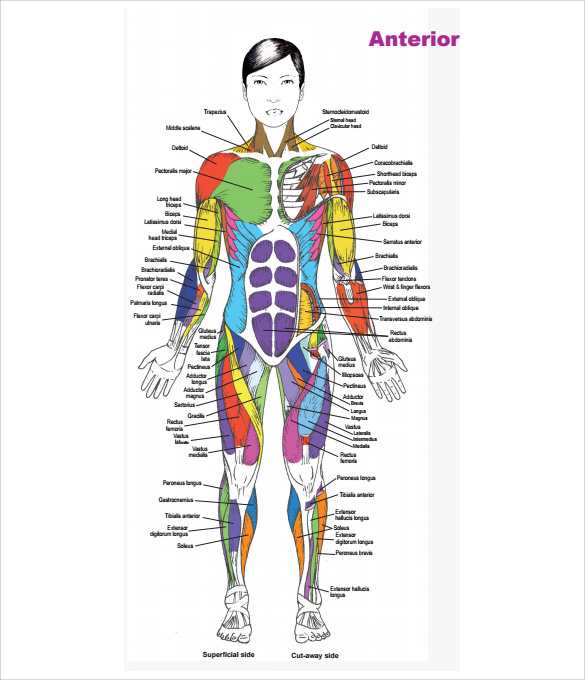
Muscle Origin And Insertion Chart
Muscle Origin And Insertion Chart - Occipital bone and spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae. Web axial muscles originate on the axial skeleton (the bones in the head, neck, and core of the body), whereas appendicular muscles originate on the bones that make up the body’s limbs. Web the muscle origin often describes the more proximal attachment point of the muscle, while the muscle insertion point refers to the distal attachment. Web the origin is the location where a muscle attaches to a fixed (or stabilized) bone with respect to the joint the muscle is acting on. Muscles from lab pack with actions, origins and insertions: Muscle name origin insertion action innervation. A muscle’s origin is usually at the attachment of its tendon to the bone with greater mass and stability. If the place is on the bone that moves. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Web the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Finally, a reliable source (and good looking too!). The muscles of the anterior neck are arranged to facilitate swallowing and speech. Muscles from lab pack with actions, origins and insertions: Muscle origins and insertions can be described as the anchor end [origin] and the most mobile end [insertion] when the muscle shortens. Opening the mouth, sliding the lower jaw right and left. There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: Occipital bone and spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae. Mastoid process of temporal bone. This document provides information on back muscles including their origin, insertion, action, and innervation. Web the muscle origin is considered the anchor or start point of the muscle, usually located on the immovable (or less movable) bone, while the muscle insertion refers to the endpoint, attached to the bone that will be moved when the muscle contracts. Finally, a reliable source (and good looking too!). Stabilizes, elevates, retracts, rotates scapula. Web muscles that flex. Occipital bone and spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like pectoralis major/ located in the arm, clavicle, sternum, and costal cartilages of upper ribs, humerus and more. Web the muscles are named after their functions, with the flexor muscle medial most, the abductor lateral most, and the opponens muscle lying. Pressing cheek inward, compressing air while blowing. Keep in mind that to describe an action, you must name the movement, and name either the part of the body that is moving or the joint at which the movement occurs. Web the muscles are named after their functions, with the flexor muscle medial most, the abductor lateral most, and the opponens. Web the origin is the location where a muscle attaches to a fixed (or stabilized) bone with respect to the joint the muscle is acting on. Stabilizes, elevates, retracts, rotates scapula. If the place is a bone that remains immobile for an action, the attachment is called an origin. The muscles of the anterior neck are arranged to facilitate swallowing. Web remember pad (plantar interossei adduct) and dab (dorsal interossei abduct), and logic will tell you where these muscles must insert plantaris above the lateral femoral condyle (above the lateral head of gastrocnemius) Web to use and fully illustrated with more than 500 drawings, this compact reference provides a complete profile for each muscle, clearly showing its origin, insertion, nerve. Muscles from lab pack with actions, origins and insertions: Opening the mouth, sliding the lower jaw right and left. In our cheat sheets, you’ll find the origin (s) and insertion (s) of every muscle. Web a skeletal muscle attaches to bone (or sometimes other muscles or tissues) at two or more places. Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Extends hip, flexes knee, laterally rotates leg. Muscle origins and insertions can be described as the anchor end [origin] and the most mobile end [insertion] when the muscle shortens. Abduct and palmar interosseous mm. Finally, a reliable source (and good looking too!). Keep in mind that to describe an action, you must name the movement, and name either the part of the body that is moving or the joint at which the movement occurs. If the place is on the bone that moves. Web each muscle has an origin and an insertion point. The location where the muscle attaches to the bone. Bilateral contraction flexes head at neck; Acromion, spine of scapula, lateral third of clavicle. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location. Web the origin is the location where a muscle attaches to a fixed. Stabilizes, elevates, retracts, rotates scapula. Web the only one of the muscles of mastication that opens the mouth; Crest of greater tubercle (lateral. Extends hip, flexes knee, laterally rotates leg. Occipital bone and spinous processes of cervical and thoracic vertebrae. Web the muscle origin often describes the more proximal attachment point of the muscle, while the muscle insertion point refers to the distal attachment. Pressing cheek inward, compressing air while blowing. The muscle arises mainly from the flexor retinaculum and tubercle of the trapezium and inserts onto the proximal phalanx or metacarpal of the thumb. There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: Web the muscles are named after their functions, with the flexor muscle medial most, the abductor lateral most, and the opponens muscle lying deep. If the place is on the bone that moves. Unilateral contraction bends neck towards shoulder or laterally rotates head. Muscles from lab pack with actions, origins and insertions: Web to use and fully illustrated with more than 500 drawings, this compact reference provides a complete profile for each muscle, clearly showing its origin, insertion, nerve supply, and action, the movements that use it, and, where appropriate, exercises that. Finally, a reliable source (and good looking too!). Web the muscle origin is considered the anchor or start point of the muscle, usually located on the immovable (or less movable) bone, while the muscle insertion refers to the endpoint, attached to the bone that will be moved when the muscle contracts. Keep in mind that to describe an action, you must name the movement, and name either the part of the body that is moving or the joint at which the movement occurs. Medial half of clavicle, front of sternum, costal. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like pectoralis major/ located in the arm, clavicle, sternum, and costal cartilages of upper ribs, humerus and more. Learn with flashcards, games, and more — for free. The muscles of the anterior neck are arranged to facilitate swallowing and speech.SOLUTION Muscle origin insertion and action list charts Studypool
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Chart amulette
MUSCLE CHART WITH ORIGIN AND INSERTION
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Chart amulette
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Chart amulette
Muscle Origin and Insertions Muscles of Mastication Muscle Origin
Chart of Muscle Origin Insertion Action
Muscle Origin And Insertion Chart
FREE 7+ Sample Muscle Chart Templates in PDF
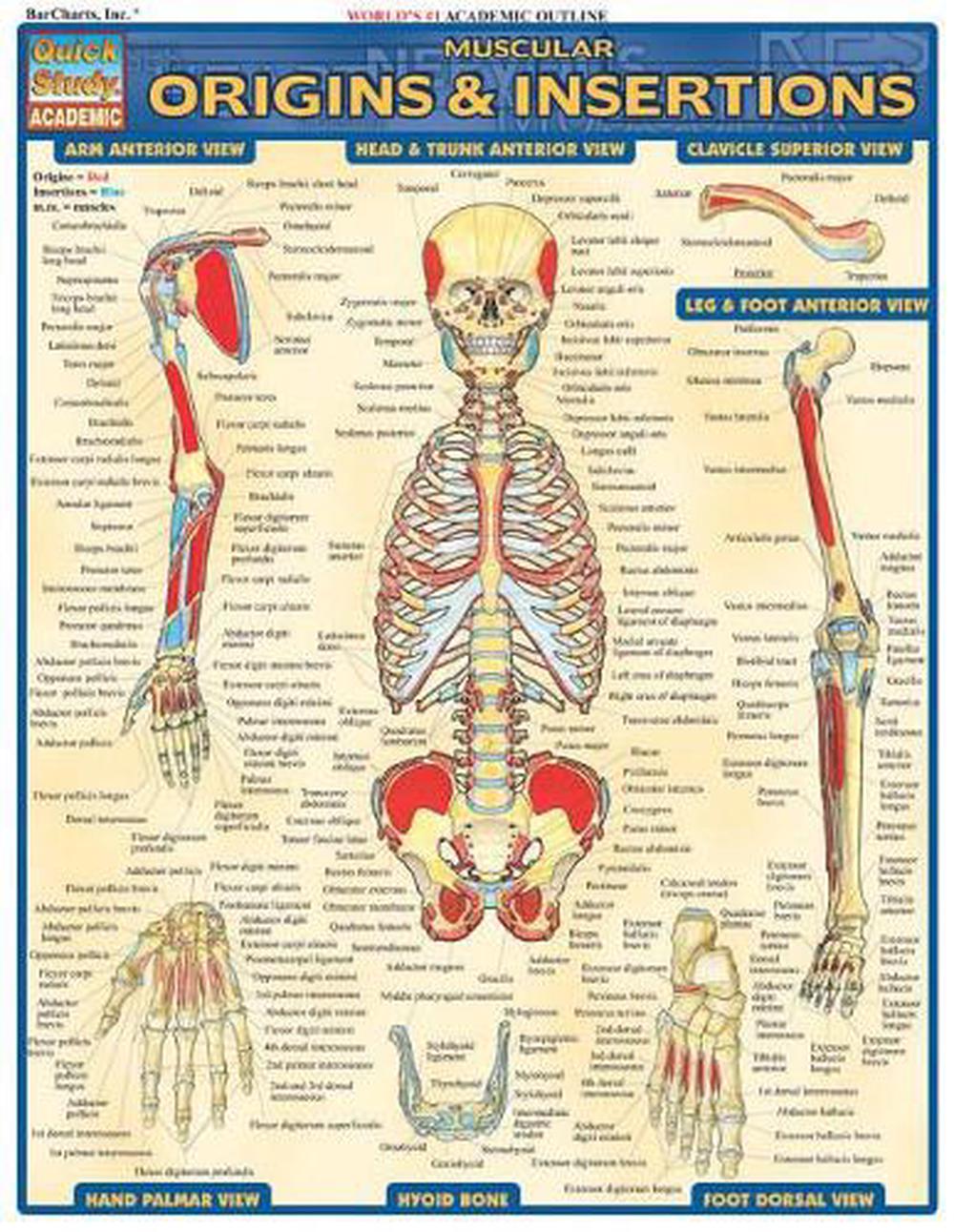
Muscular Origins & Insertions Laminate Reference Chart by Inc BarCharts
Web Axial Muscles Originate On The Axial Skeleton (The Bones In The Head, Neck, And Core Of The Body), Whereas Appendicular Muscles Originate On The Bones That Make Up The Body’s Limbs.
In Our Cheat Sheets, You’ll Find The Origin (S) And Insertion (S) Of Every Muscle.
Opening The Mouth, Sliding The Lower Jaw Right And Left.
This Document Provides Information On Back Muscles Including Their Origin, Insertion, Action, And Innervation.
Related Post: